The geothermal heat pumps market is witnessing significant growth as the world increasingly turns to sustainable and energy-efficient solutions for heating and cooling systems. Geothermal heat pumps, which utilize the stable temperatures beneath the earth's surface to provide energy-efficient heating and cooling, have emerged as a popular choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. With the growing demand for renewable energy sources and the need to reduce carbon emissions, the geothermal heat pumps market is expected to continue its upward trajectory. In this article, we will explore the key drivers, challenges, and future prospects of the geothermal heat pumps market.
What are Geothermal Heat Pumps?
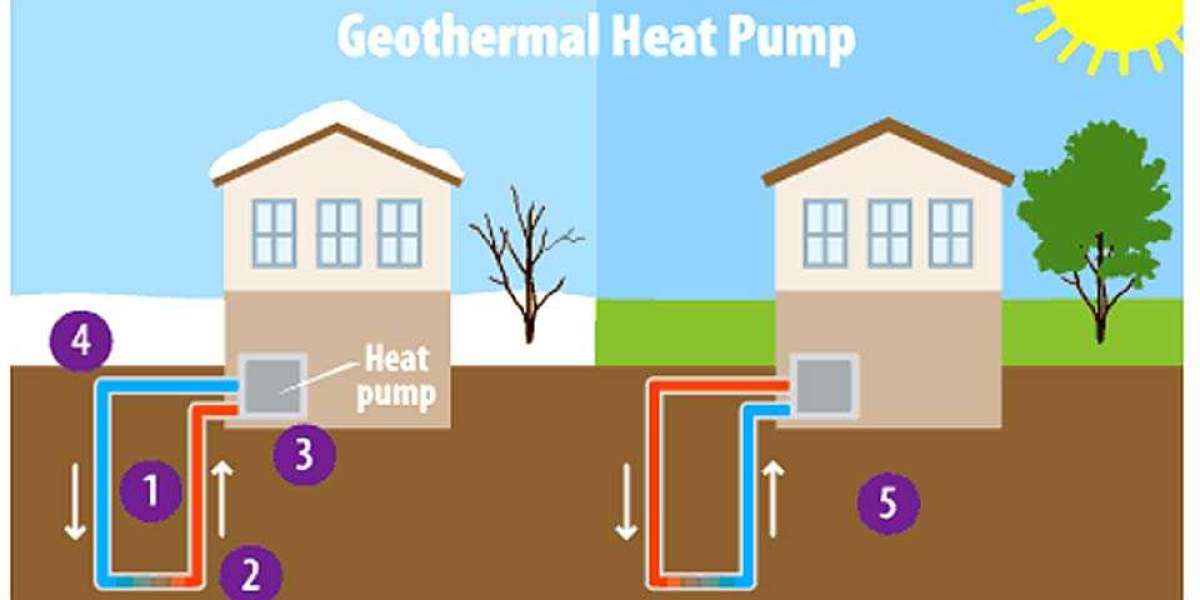
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) are systems that leverage the earth's natural temperature to heat and cool buildings. These systems consist of a heat pump, an air delivery system (ductwork), and a heat exchanger — a system of pipes buried in the shallow ground near the building. The earth maintains a relatively constant temperature of about 50°F (10°C) to 60°F (15°C) a few feet below the surface, making it an ideal medium for heat exchange. In winter, geothermal heat pumps extract heat from the ground and transfer it into the building; in summer, the process is reversed, and the system pulls heat from the building and releases it into the cooler ground.
Geothermal heat pumps are known for their high efficiency and low operating costs compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. They are considered one of the most environmentally friendly HVAC solutions available today, as they use renewable energy from the earth’s core, reducing the need for fossil fuels.
Key Drivers of the Geothermal Heat Pumps Market
1. Growing Demand for Energy-Efficient Solutions
One of the primary factors driving the geothermal heat pumps market is the increasing global demand for energy-efficient solutions. As consumers and businesses look to reduce their energy consumption and lower operating costs, geothermal heat pumps offer an attractive alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. These systems consume less electricity, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective over the long term, despite the higher initial installation costs.
2. Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
With growing concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability, governments, organizations, and individuals are seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprints. Geothermal heat pumps contribute to this effort by offering a renewable energy solution that significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike conventional HVAC systems that rely on fossil fuels, geothermal heat pumps use the earth’s natural heat, making them a clean and green alternative. This sustainability factor is a major driver in the geothermal heat pumps market, as many countries and regions are introducing policies and incentives to promote renewable energy adoption.
3. Government Incentives and Subsidies
Many governments around the world have recognized the environmental and economic benefits of geothermal energy and are offering financial incentives, tax rebates, and subsidies to encourage the adoption of geothermal heat pumps. For instance, in the United States, the federal government provides a tax credit for residential and commercial geothermal heat pump installations under the Energy Policy Act. Similarly, in Europe, countries like Germany, Sweden, and the Netherlands offer financial support for renewable heating technologies, further fueling the growth of the geothermal heat pumps market.
4. Rising Adoption of Green Building Practices
As part of the global trend toward sustainability, there is a growing demand for green buildings, which are designed to minimize environmental impact and maximize energy efficiency. Geothermal heat pumps are an essential component of green building technologies, as they offer a low-carbon alternative to conventional heating and cooling systems. With building codes becoming more stringent and energy-efficient design practices gaining traction, the geothermal heat pumps market is poised for substantial growth.
Types of Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps come in several configurations, each suitable for different types of installations and requirements. The three main types include:
1. Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop geothermal systems are the most common type of geothermal heat pump installations. These systems use a closed loop of piping buried in the ground to circulate a heat transfer fluid (usually water or an antifreeze solution). The loop can be installed horizontally or vertically, depending on the available land area and the specific needs of the installation. Horizontal loops are more commonly used in residential applications where there is ample land space, while vertical loops are typically used in urban or commercial settings where land is limited.
2. Open-Loop Systems
Open-loop geothermal systems use water from a well, pond, or other water source to circulate through the system. The water is extracted from the source, passes through the geothermal heat pump system to exchange heat, and then returns to the water source. This type of system is less common than closed-loop systems, as it requires a consistent and sustainable water supply. Additionally, open-loop systems may require more maintenance and regulatory approval due to concerns over water usage and potential contamination.
3. Hybrid Systems
Hybrid geothermal systems combine the benefits of both geothermal heat pumps and conventional heating and cooling technologies. These systems are designed to operate alongside traditional HVAC systems, providing energy-efficient heating and cooling while also utilizing other energy sources such as natural gas or electricity when needed. Hybrid systems are often used in situations where the energy demands of a building fluctuate or where there are concerns about the initial installation costs of a full geothermal system.
Regional Insights: Geothermal Heat Pumps Market by Region
North America
North America, particularly the United States and Canada, is a significant market for geothermal heat pumps. The U.S. has a well-established geothermal industry, and government incentives such as tax credits and grants have encouraged widespread adoption of geothermal systems in both residential and commercial applications. Canada, too, has seen increased interest in geothermal heating and cooling systems, driven by the country's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy efficiency.
Europe
Europe is one of the largest markets for geothermal heat pumps, with countries like Sweden, Germany, and Switzerland leading the way. Geothermal energy is a key part of the European Union's renewable energy strategy, and many European countries have implemented regulations and incentives to promote the use of geothermal heat pumps. In particular, Sweden has become a global leader in geothermal energy use, with a high penetration rate of geothermal heat pumps in residential and commercial buildings.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as a high-growth market for geothermal heat pumps, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing energy demands, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are adopting geothermal technologies as part of their broader efforts to reduce carbon emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources. Japan, in particular, has seen a surge in the use of geothermal heat pumps due to the country's strong commitment to renewable energy and energy efficiency.
Latin America
In Latin America, the geothermal heat pumps market is still in its early stages but is expected to grow as governments focus on diversifying their energy portfolios and promoting green technologies. Countries such as Brazil and Mexico are exploring the potential of geothermal energy and heat pump systems as part of their renewable energy strategies.
Challenges in the Geothermal Heat Pumps Market
Despite the numerous benefits, the geothermal heat pumps market faces some challenges:
1. High Initial Installation Costs
One of the main barriers to widespread adoption of geothermal heat pumps is the high upfront installation cost. Although the systems provide significant long-term savings on energy bills, the initial investment can be prohibitive for many consumers, particularly in residential settings. The cost of drilling, equipment, and installation can be substantial, although government incentives and rebates can help offset these costs.
2. Limited Awareness and Education
In many regions, there is still limited awareness about the benefits and advantages of geothermal heat pumps compared to traditional HVAC systems. Education and outreach efforts are essential to help consumers understand how geothermal systems work, the long-term savings they offer, and their environmental benefits.
3. Site and Soil Conditions
Geothermal heat pump systems require specific site and soil conditions to function optimally. Factors such as ground composition, the availability of land, and local geology can influence the efficiency of the system. In areas with unsuitable soil or insufficient space, installing a geothermal system may not be feasible, limiting the market potential in certain regions.
Future Outlook of the Geothermal Heat Pumps Market
The geothermal heat pumps market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. Several factors will contribute to this expansion:
Technological advancements in geothermal systems will improve efficiency and reduce installation costs.
Government policies and incentives will continue to promote the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
Increased demand for sustainable building practices will drive the integration of geothermal heat pumps in new construction projects.
In conclusion, the geothermal heat pumps market is positioned for strong growth as the world seeks more sustainable, energy-efficient solutions. With ongoing advancements in technology, supportive policies, and an increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions, geothermal heat pumps are expected to play a key role in the global transition to renewable energy.
More Trending Reports